Natural Disasters
Definition: A natural disaster is the consequence of the combination of a natural hazard (a physical event like a volcanic eruption,typhoon, tropical cyclone tornado, an earthquake, a landslide or a tsunami) and human activities.
Most natural disasters are caused by weather.

- hurricane, can be predicted, it is a tropical cyclone.
- tornados ,
- floods, most expensive type of natural disaster
- tsunamis,
- thunderstorms
- wind storms,
- wildfire, caused by lightning or by people
- avalanches, and
- blizzards, can be predicted
- volcanoes and
- Earthquakes, deadliest of all natural disasters.
- Some of the weather disasters can be predicted such as hurricanes and blizzards. The technology is getting better in predicting tornadoes and severe thunderstorms. By getting the data early people can be warned to take shelter or make the necessary preparations.
- Some natural disasters are caused by volcanoes and earthquakes.
- Some wildfires are caused by lightning, but some are caused by people
- Flooding is the world's most expensive type of natural disaster because the damage can be extensive
- Earthquakes are the deadliest of all natural disasters
- Some kinds of disasters are more common in some places then in others when people are choosing a place to live they need to consider whether they will live on a fault line for an earthquake or near a river that has a history of flooding.
- There isn't any way to avoid natural disasters but if people know what kinds of disasters are most likely where they live they can learn what to do if a disaster happens in order to stay safe
- Many different agencies such as the red cross and red crescent come to the assistant of people affected by natural disasters.
Hurricane, can be predicted, it is a tropical cyclone.

- Large movements cause the waves to be formed, making waves.
- These waves travel across the ocean to affect distant lands, at great speed (500 miles per hour). Wonder if your car can drive this fast. Not, me thinks.
- When the waves approach the shallow waters they pile up and grow in height. Monstrously terrorising the poor beach goers, and old folks.
- At the coastline - the trough pulls the water back, and these crest of the wave grows higher and higher, ready to smack the shore. Please don't play in the receding waters, you may be smacked by the growing 300 meter crest. Good to pray before this happens, it may be the last thing you do.
- Japan is not popular because of its frequent Tsunamis. Nice people though. Love to JAPAN. Pacific Ocean. Indian Ocean Tsunami of 2004 killed 230000 people. That really ruined alot of Christmas holidays.
- Tsunamis can cause major damage, like a city being hit by a really big bus.
- Early warning systems for Tsunamis help people get to higher ground. I think these discriminate against people with hearing impairments.
Earthquakes, deadliest of all natural disasters.
Definition of Earthquakes: a sudden violent shaking of the ground, typically causing great destruction, as a result of movements within the earth's crust or volcanic action.
The rapid release energy is released from the earths crust, causes seismic waves that travel through the earth.
facts on earthquakes:
- Earthquakes involve the powerful movement of rocks in the Earth’s crust. The rapid release of energy creates seismic waves that travel through the earth.
- Scientists use the different speeds of seismic waves to locate the epicentre (the point on the surface directly above where the earthquake originated) of earthquakes.
- Seismometers are used to measure the magnitude of earthquakes. You are unlikely to feel a magnitude 3 earthquake but a magnitude 6 earthquake could potentially cause large damage.
- The damage caused by earthquakes also depends on their depth and fault type.
- The earthquake that hit the Tohoku region of Japan on March 11, 2011, had a magnitude of 9.0 and killed over 15000 people.
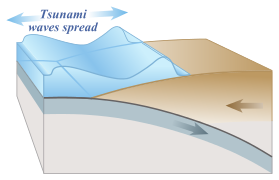
- The destruction caused by the Tohoku earthquake was made much worse by powerful tsunamis that were triggered due to the earthquake’s epicentre being located offshore. More tsunami facts.
- The 2004 earthquake that occurred in the Indian Ocean near Sumatra, Indonesia triggered a series of tsunamis that killed over 200000 people in 14 countries.
- The February 2011 earthquake in Christchurch, New Zealand followed nearly 6 months after a magnitude 7.1 earthquake shook the region. The earthquake killed 181 people and significantly damaged the central city. The economic damage caused by the earthquake and aftershocks is estimated to be around $15 billion (NZ$).
- An earthquake that hit Haiti in January 2010 with a magnitude of 7.0 killed over 200000 people according to Haitian sources.
- The most powerful earthquake ever recorded on Earth was in Valdivia, Chile. Occurring in 1960, it had a magnitude of 9.5.
- It is important in earthquake prone countries such as Japan to build houses and buildings that react well to earthquakes. Good engineering practises can help stop buildings collapsing under the stress of large earthquakes.
how does it occur:
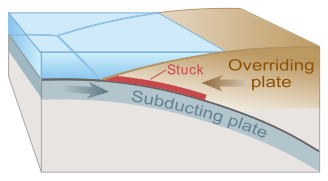
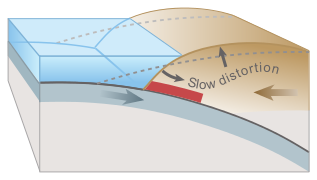
Earthquakes are usually caused when rock underground suddenly breaks along a fault. This sudden release of energy causes the seismic waves that make the ground shake. When two blocks of rock or two plates are rubbing against each other, they stick a little. They don't just slide smoothly; the rocks catch on each other. The rocks are still pushing against each other, but not moving. After a while, the rocks break because of all the pressure that's built up. When the rocks break, the earthquake occurs. During the earthquake and afterward, the plates or blocks of rock start moving, and they continue to move until they get stuck again. The spot underground where the rock breaks is called the focus of the earthquake. The place right above the focus (on top of the ground) is called the epicenter of the earthquake.



No comments:
Post a Comment